When it comes to search engine optimization (SEO), most marketers focus on high-volume keywords, backlinks, and content creation. But often overlooked in the SEO toolkit is a strategy that’s both incredibly powerful and completely within your control: internal linking.
A strong internal linking strategy can significantly boost your site’s crawlability, distribute link equity, improve user experience, and, most importantly, enhance your rankings. In 2025, with Google’s algorithms placing even greater emphasis on content relationships and semantic understanding, internal linking has become an SEO goldmine that too many still ignore.
What Is Internal Linking?
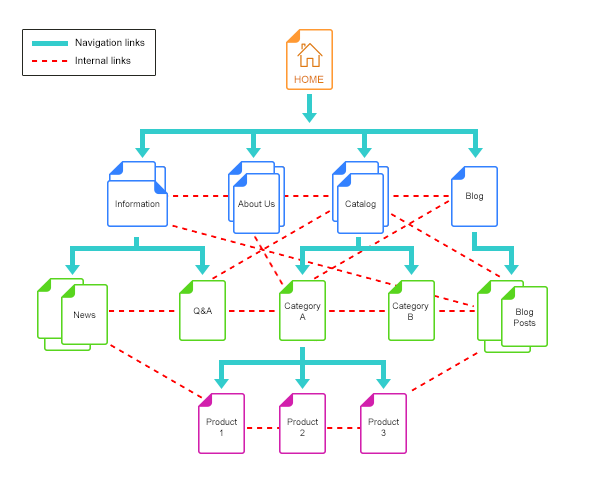
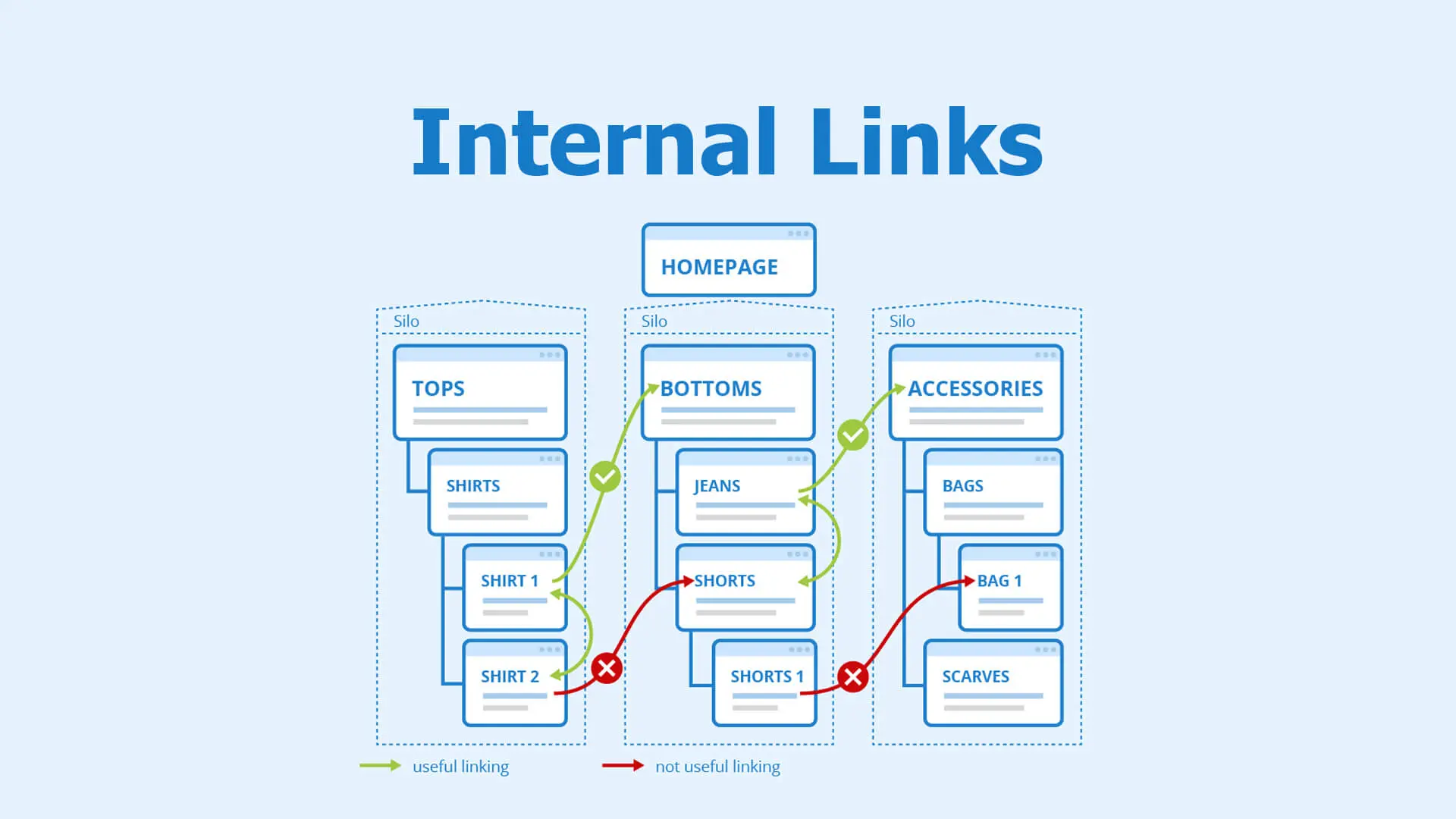
Internal linking refers to the practice of linking from one page on your website to another page on the same domain. Unlike external links, which point to different domains, internal links keep users (and crawlers) within your ecosystem.
Common types of internal links include:
- Navigational links (menus, footers)
- Contextual links within content
- Related posts/products recommendations
- Breadcrumbs
- Calls-to-action (CTAs) that drive users to key pages
The key is to create a logical structure that connects your content in a meaningful and SEO-friendly way.
Why Internal Linking Is So Valuable
1. Distributes Page Authority (Link Equity)
Internal links help spread authority from high-performing pages (such as ones with external backlinks) to others that need a boost. If you have a blog post that ranks well and has earned links, linking it to a product page or a related article can elevate those pages too.
2. Improves Crawlability and Indexation
Search engine bots use internal links to discover and index pages. A well-structured internal link system ensures that deep pages don’t get buried and overlooked. Pages without internal links—commonly known as orphan pages—are often invisible to search engines.
3. Enhances Relevance Through Contextual Signals
Google uses internal links to understand how content relates across a site. Using relevant anchor text in your links helps clarify the semantic connection between pages and reinforces topical authority.
4. Boosts User Engagement
Internal linking improves user experience by guiding visitors to related content. This increases time on site, pages per session, and reduces bounce rates—positive engagement signals for SEO.
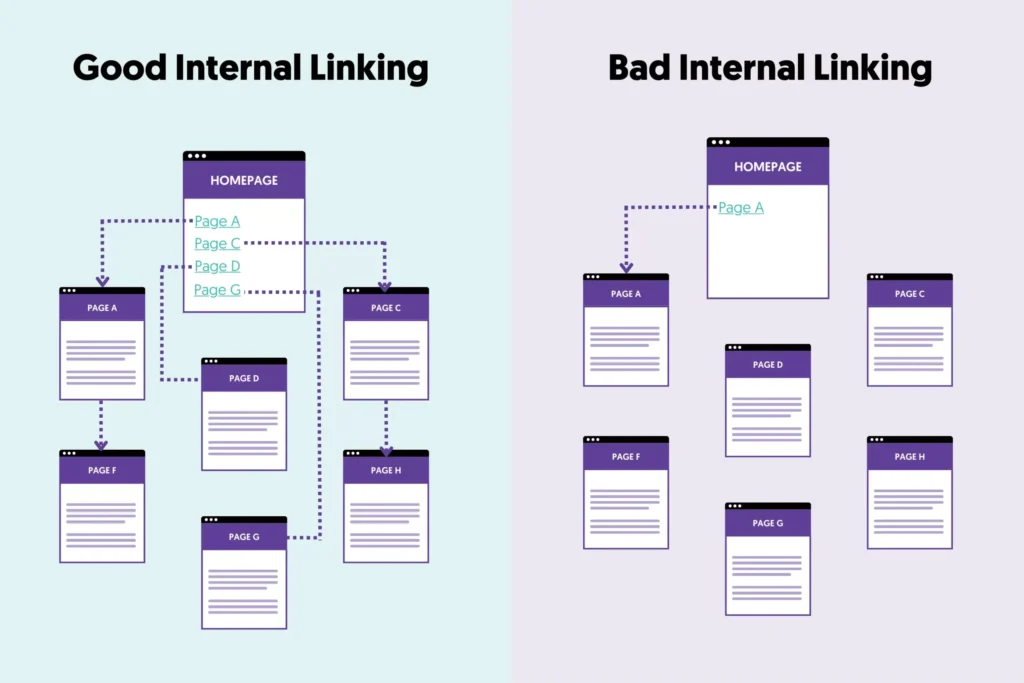
Building an Effective Internal Linking Strategy
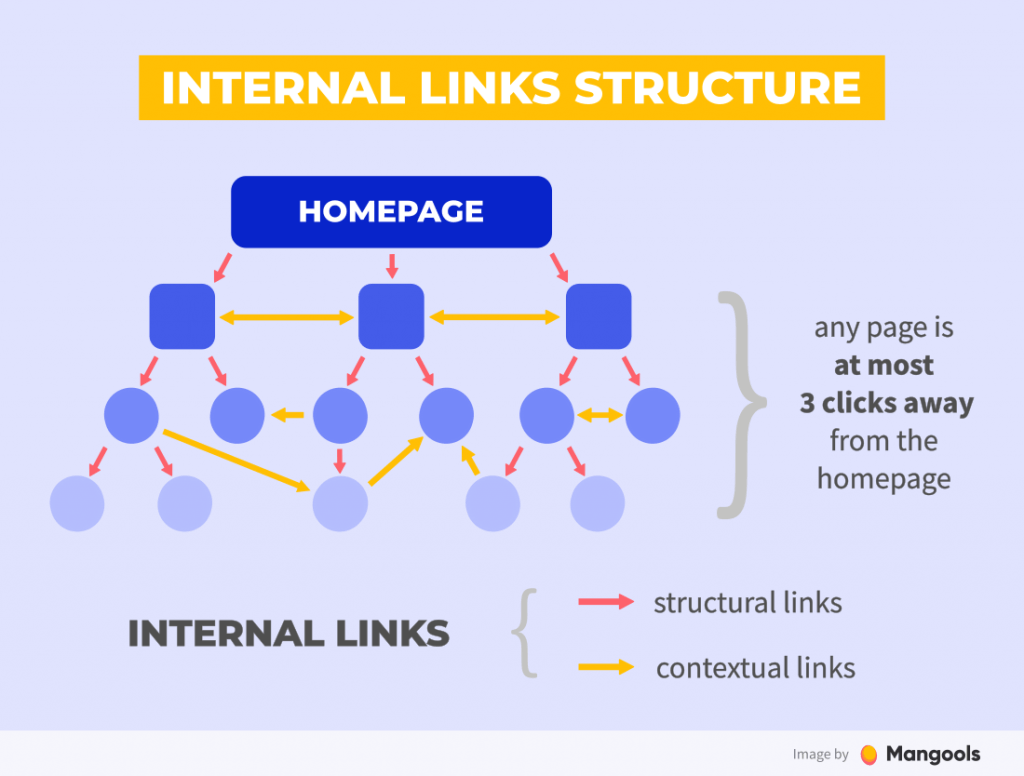
1. Start with a Clear Site Hierarchy
Organize your content in a pyramid structure:
- Homepage at the top
- Category or silo pages in the middle
- Individual content or product pages at the base
Each page should link upward and downward within its silo, keeping themes tightly connected.
2. Use Descriptive, Keyword-Rich Anchor Text
Avoid generic terms like “click here” or “read more.” Instead, use anchor text that reflects the target page’s topic. For example:
- Instead of: Click here for our tips.
- Use: Check out our on-page SEO best practices guide.
This reinforces keyword relevance and helps Google understand page context.
3. Prioritize High-Value Pages
Use tools like Google Analytics and Ahrefs to identify your top-performing pages. Link from these to newer or lower-performing content to pass authority and drive traffic.
4. Fix Orphan Pages
Crawl your site with tools like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb to identify pages that have no internal links pointing to them. These pages are often neglected by search engines and users alike.
5. Context Over Quantity
More links aren’t always better. One strategically placed, contextually relevant link is more valuable than a dozen random ones. Keep the user journey in mind and make the links feel natural.
6. Use Topic Clusters and Pillar Pages
Group related content under a main “pillar” page that acts as a hub. All subtopics link back to the pillar, and the pillar links out to each subtopic. This creates a network that boosts topical authority.
7. Automate Where Possible
Plugins like Link Whisper (for WordPress) use AI to suggest internal links as you write. While automation can help speed up the process, always review suggested links to ensure relevance and accuracy.
Tools to Optimize Internal Linking
- Ahrefs: Use the “Best by links” and “Internal backlinks” reports to find opportunities.
- Google Search Console: Track how well pages are linked internally and see which ones have low link value.
- Screaming Frog: Perform site audits to identify orphan pages, broken internal links, and opportunities for improved linking.
- Surfer SEO & Clearscope: Identify keyword-rich phrases for anchor text opportunities.
- Link Whisper (WordPress): Automates internal link suggestions and tracking.
Common Internal Linking Mistakes to Avoid
- Over-optimizing anchor text: Using exact match anchors excessively can trigger penalties. Vary your phrasing naturally.
- Linking just for the sake of it: Every link should serve a purpose—guide the user, reinforce the topic, or support conversion.
- Broken or redirected links: These hurt crawlability and user experience. Regularly audit and fix them.
- Too many links on a page: This dilutes link equity. Focus on linking to the most relevant and important pages.
Real-World Example: Internal Linking Done Right
A SaaS company builds a content hub around “Remote Work Tools.” The pillar page targets that keyword and links to subpages like:
- “Best Video Conferencing Software”
- “Time Tracking Apps for Remote Teams”
- “Managing Productivity in Remote Workplaces”
Each subpage links back to the pillar and cross-links to each other where relevant. Over time, the pillar page climbs in rankings for “Remote Work Tools,” and the subpages rank for their respective topics, reinforcing the entire content ecosystem.
Conclusion
Internal linking is one of the most underused and undervalued strategies in SEO—despite its enormous potential. It costs nothing, is fully within your control, and can deliver measurable improvements in rankings, crawlability, and engagement.
As SEO becomes more semantic and user-focused in 2025, a strategic internal linking structure does more than pass link juice—it signals authority, relevance, and intent. Treat it as an essential part of your SEO playbook, not an afterthought, and you’ll uncover a goldmine hiding in plain sight.